Fuzzy Automatic Guided Vehicle
There are always various kinds of disturbances in the environment that causes the
instability of the Automatic Guided Vehicle (AGV). The position error is aroused
because the trajectory can not follow the reference trace accurately. In this application
a fuzzy control scheme is proposed based on the analysis of the kinematics equation
and the trajectory error of AGV. Then, simulations are made with the white noise
instead of the disturbances. Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed
fuzzy control strategy can improve the kinematics performance of AGV significantly.
The Automatically Guided Vehicle (AGV) is a typical element of the group of materials
handling equipment. A popular way of AGV guidance is based on the guide path method.
The guide path is usually a painted marking or a passive or active wire (guidewire)
glued onto or built into the floor. The goal of the steering part of the guidance
system of the AGV is to follow the marking of the guide path. The guiding system
senses the position of the guide path by special sensors (guide zone) tuned for
the guide path. The guide zone is a section of the AGV determined by the guide path
sensor (or raw of sensors). The goal of the steering control is to follow the guide
path by the guide zone with minimal path tracking error on the whole path.
The kinematic of the AGV is determined by its wheel configuration. The AGVs without
fixed directional wheels in their wheel configuration can be moved to arbitrary
direction. While the AGVs with at least one fixed directional wheel can run only
on a path curve has its momentary centre on the line fits the axe of the fixed directional
wheel. In the further part of this article we would like to concentrate on the path
tracking strategy of a differential steered AGV which has fixed directional wheel.
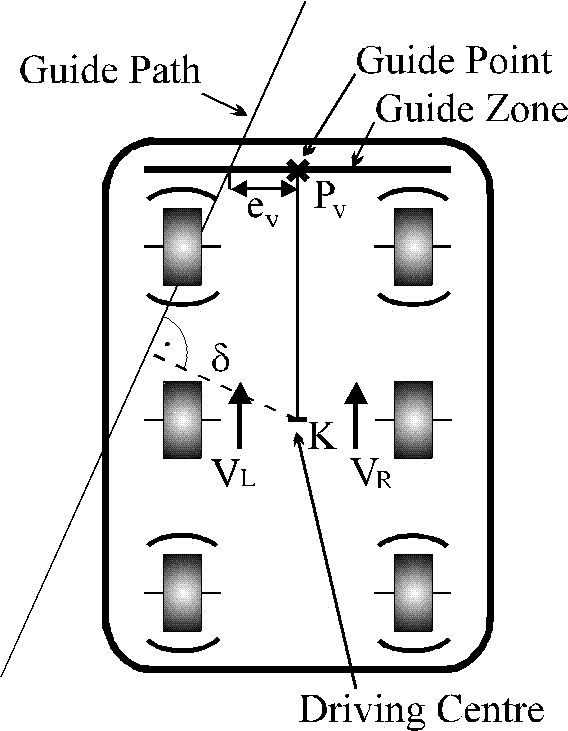
Differential steered AGV with guide zone, δ is the path tracking error, ev is the
distance of the guide path and the guide point, Pv is the guide point, K is the
driving centre, UL, UR, UM are the left, right and middle ultrasonic distance sensors.